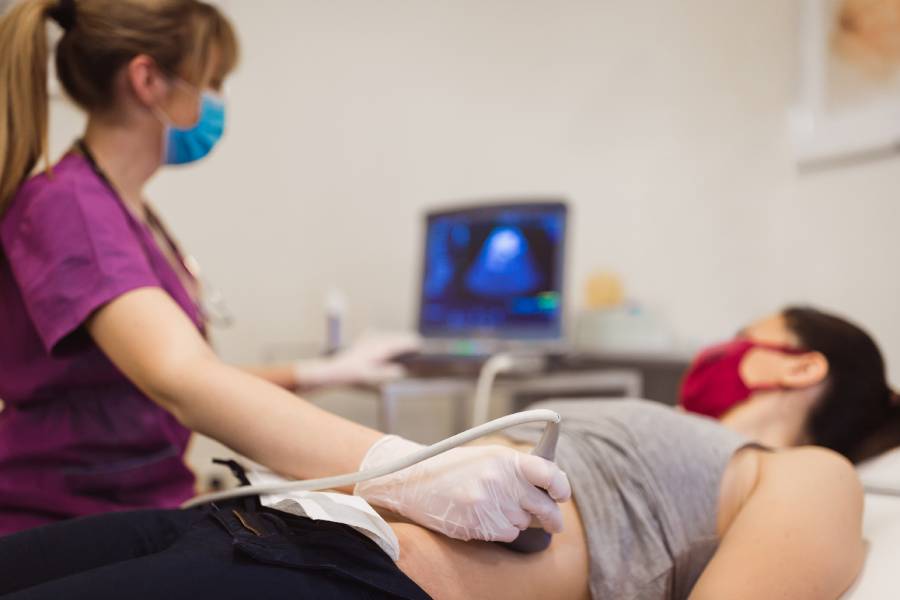
What Is Sonography?
Sonography is a diagnostic medical test that uses sound waves to assess the internal body organs and capture them in a pictorial form. It is a painless and non-invasive test. Sonography does not use any form of radiation and is hence, relatively a safe test. The image created is known as a sonogram. The test is also referred to as ultrasound imaging.
What Are the Various Types of Ultrasound?
Diagnostic ultrasounds are categorized into four main types:
- Conventional: A conventional ultrasound is the most frequently advised test. It results in a simple two-dimensional black-and-white image.
- 3-D Ultrasound: The image is received in a three-dimensional format.
- 4-D Ultrasound: It is a three-dimensional image in motion.
- Doppler Ultrasound: It is a specialized ultrasound technique that is used to assess blood flow. It can be depicted as a color image or even be heard as a unique sound that can be recorded and evaluated.
What Are the Uses of Sonography?
Sonography has distinctive uses based on the anatomical areas of the body where it is used;
1. Head and Neck:
- Any pain, swelling, or infection can be diagnosed using ultrasound.
- Sonography is used in diagnosing salivary gland diseases, thyroid anomalies, neurological disorders, and other head and neck tumors.
- The extent of oral cancer and its lymphatic spread can easily be detected with ultrasound.
2. Breast:
- Sonography is the first-line test in cases of a lump in the breast. It also aids in biopsies.
3. Heart:
- Ultrasound is used to diagnose various cardiac conditions such as congestive heart disease and valvular heart disease.
- Doppler tests may be used to detect any vessel blockages.
4. Lungs:
- A chest ultrasound helps in visualizing the lungs, trachea, esophagus, and associated lymph nodes.
- Pleural effusion, tumors, and pneumonia can be diagnosed using ultrasound.
5. Abdomen and Pelvis:
- Ultrasound can be used to examine the liver, kidney, gallbladder, uterus, ovaries, prostate, pancreas, spleen, and other internal organs.
- Any anomalies, altered blood flow, cysts, or tumors in the above organs can easily be detected using ultrasound.
6. Pregnancy:
- Ultrasound is the confirmatory pregnancy test.
- It is used to check fetal gestational age.
- It can be used for fetal sex determination.
- It is the ultimate tool for prenatal screening; to check for birth defects, congenital anomalies, placental problems, and amniotic fluid-related challenges.
- Any pregnancy complications like ectopic pregnancies and miscarriages are earliest detected using sonography.
- Sonography also helps to identify a baby’s position; if it is in a breech position or favorable for natural birth.
What Are the Preparations Required Before Sonography?
- The preparations for the procedure will vary according to the type of sonography being performed.
- Abdomen and pelvis sonography requires a full bladder. Hence patients are advised to drink plenty of water and avoid urinating for 2 hours before the scan.
- If any comorbidities are present, a routine blood test may be instructed by the referring physician.
- Certain ultrasounds may also require fasting a few hours before the test.
- Patients will be advised to wear comfortable loose clothing before the procedure.
- Any ornaments or accessories in the concerned area need to be removed.
- Any prescription drug or over-the-counter medicine taken by the patient before the test should be informed to the radiologist.
How Is the Procedure Done?
- Sonography is usually conducted by a radiologist or trained personnel.
- Once patient preparations are done, they would be asked to lie on their back or side of the table.
- The area to be examined will be exposed.
- A water-based gel will be applied to the skin over the area to be scanned.
- The transducer would be moved over the gel back and forth.
- Slight pressure may be applied, but this will not cause any discomfort.
- The images are then captured on a monitor.
- After ensuring that the procedure is complete and the desired images are obtained, the patient will be asked to clean the gel and be guided to the waiting room.
- Normal activity can be resumed by the patient after the ultrasound test unless otherwise mentioned by the physician.
- The entire procedure may take anywhere between 30 minutes to one hour.
What Are the Benefits of Ultrasound?
- It is painless and non-invasive.
- No radiation exposure.
- Easily accessible.
- Cost-effective.
What Are the Limitations of Ultrasound?
- It cannot be used for imaging bone or air-filled tissues.
- Sound waves may not be able to penetrate thick layers of fat; hence an ultrasound is not very useful in obese people.
Contact Dr. Shraddha Galgali:
Ultrasounds are considered one of the safest and least invasive procedures. They do not cause any discomfort to the patient and are very cost-effective compared to any other tests. Ultrasound has proved its usefulness in detecting and diagnosing various disorders, and its limitations are bare minimal. Efficient treatment planning requires apt diagnosis. For the best treatment call us at 9923956515 or book an online appointment